Gynecomastia
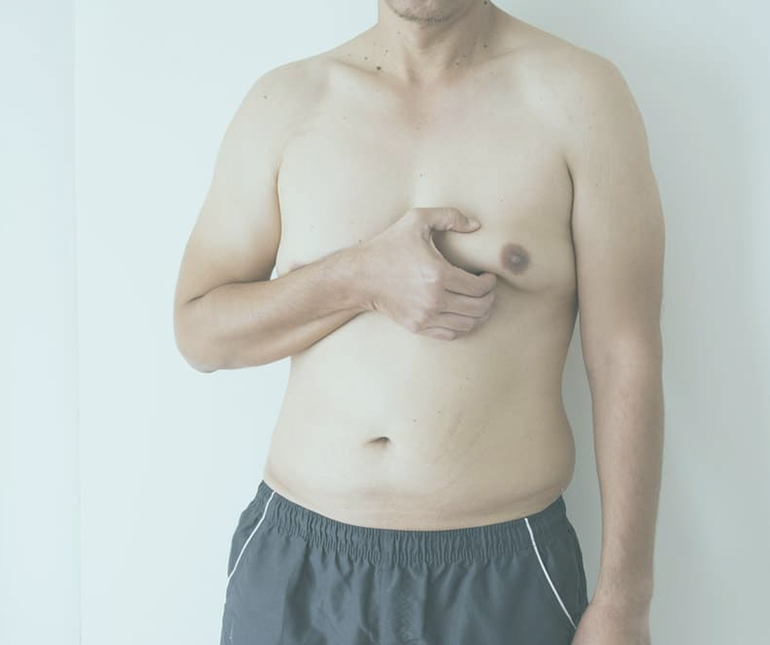
Gynecomastia is a condition of overdevelopment or enlargement of the breast tissue in men or boys. The breasts become larger. They may grow unevenly.
Gynecomastia often happens when a preteen or teenage boy is going through the hormonal changes of puberty. But it can also happen to newborn babies and to men as they age.
What causes gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is usually a benign (noncancerous) condition. It may be linked to many different causes of hormone changes. In many cases, the cause isn’t known.
Gynecomastia is often caused by changes in levels of the female hormone (estrogen) and the male hormone (testosterone). But it can be caused by other things as well.
Gynecomastia can be a side effect of certain medicines, such as antidepressants, antibiotics, chemotherapy, prostate cancer medicines, ulcer or cardiovascular medicines. Illegal drugs, such as anabolic steroids, heroin, or marijuana can also cause gynecomastia.
Some diseases and medical conditions may also cause gynecomastia. These include:
1. Liver diseases
2. Kidney disease
3. Lung cancer
4. Testicular cancer
5. Tumors of the adrenal glands or pituitary gland
6. Some conditions that a baby is born with (congenital disorders)
7. Thyroid disorders
8. Injury or trauma
9. Obesity
What are the symptoms of gynecomastia?
You may have gynecomastia in one or both breasts. It may start as a lump or fatty tissue beneath the nipple, which may be sore. The breasts often get larger unevenly.
The symptoms of gynecomastia may look like other medical conditions or problems. Always see your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
How is gynecomastia diagnosed?
Your provider will take your past health and medicine history and give you a physical exam.
To rule out other diseases or conditions, you may also have tests including:
- Blood tests, including liver function tests and hormone studies
- Urine tests
- A low-dose X-ray of your breast (mammogram)
- A small breast tissue sample (a biopsy) may be removed and checked for cancer cells